Choosing a mortgage in Quebec involves more than just the lowest interest rate. The rate is merely one contract component. Term, amortization, prepayment rules, and penalties often impact the total borrowing cost more significantly than many realize.
Buyers often compare offers based solely on the headline rate. However, two mortgages with identical rates can behave very differently. This depends on payment adjustments, contract flexibility, and consequences if plans change mid-term.
This guide explains Quebec mortgages. It covers fixed versus variable rates, term renewals, “open” and “closed” conditions, and penalty calculations for breaking or changing a mortgage. The goal is to clarify how to evaluate offers based on their real long-term impact. Also you can check the FCAC mortgage guide.
Understanding Amortization vs. Mortgage Term in Quebec
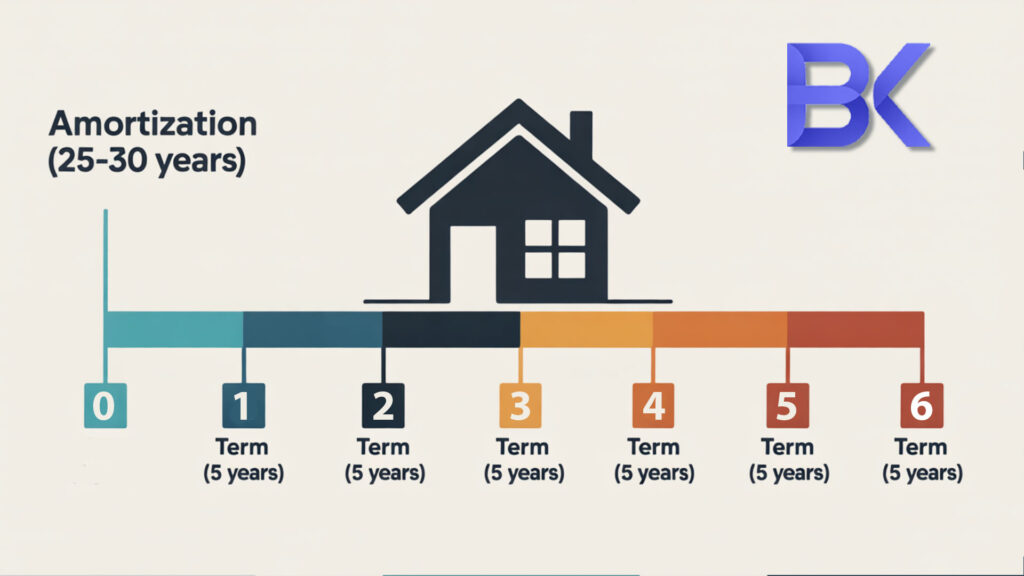
Every Canadian mortgage has two parallel timelines.
Amortization is the long-term horizon, typically 25 years for insured mortgages and up to 30 years for some conventional ones. This is the time needed to pay off the mortgage fully at the current payment schedule.
The term is the contractual period during which your rate, conditions, and lender remain fixed. Most terms last 1 to 5 years, occasionally longer. When the term ends, amortization continues, but you must renew, renegotiate, or switch lenders.
Many borrowers mistakenly consider the term the mortgage’s full life. In reality, the selected rate applies only to this short segment. Over decades, you will likely renew your mortgage several times under varying market conditions.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages: Predictable Payments in Quebec
Fixed-rate mortgages are Quebec’s most popular choice. Their appeal is simple: payments remain constant for the entire term. Once the rate is set, your monthly budget becomes fully predictable.
A fixed rate protects against rising interest rates, offering stability during economic uncertainty. For families with long planning horizons, predictable payments often outweigh potential short-term savings.
The trade-off is flexibility. If interest rates fall or you break the mortgage early, the lender may calculate a penalty using an interest rate differential (IRD). This can make fixed mortgages costly to exit before maturity, especially when rates have dropped since signing.
Fixed rates suit those planning to stay in their property for most of the term, preferring a structured, low-volatility payment schedule.
Variable-Rate Mortgages: Flexibility and Rate Fluctuations
A variable mortgage tracks the lender’s prime rate, which usually moves with the Bank of Canada’s policy rate. Depending on the lender, either your monthly payment changes, or the payment stays fixed while the interest portion adjusts. If payment stays fixed while rates rise, you hit a ‘trigger rate’ where your payment covers only interest. This is a vital risk to discuss.
Variable mortgages often start with a lower initial rate than comparable fixed options. Over time, this can lead to savings if rates remain stable or decline.
The downside is exposure to rate increases. If the prime rate rises, your payment or interest cost also increases. Borrowers must be comfortable with this movement and able to adjust their budgets if payments fluctuate.
Variable mortgages typically incur lower penalties for early termination, often just three months’ interest. This makes them attractive for buyers expecting to move, refinance, or restructure before a standard five-year term ends.
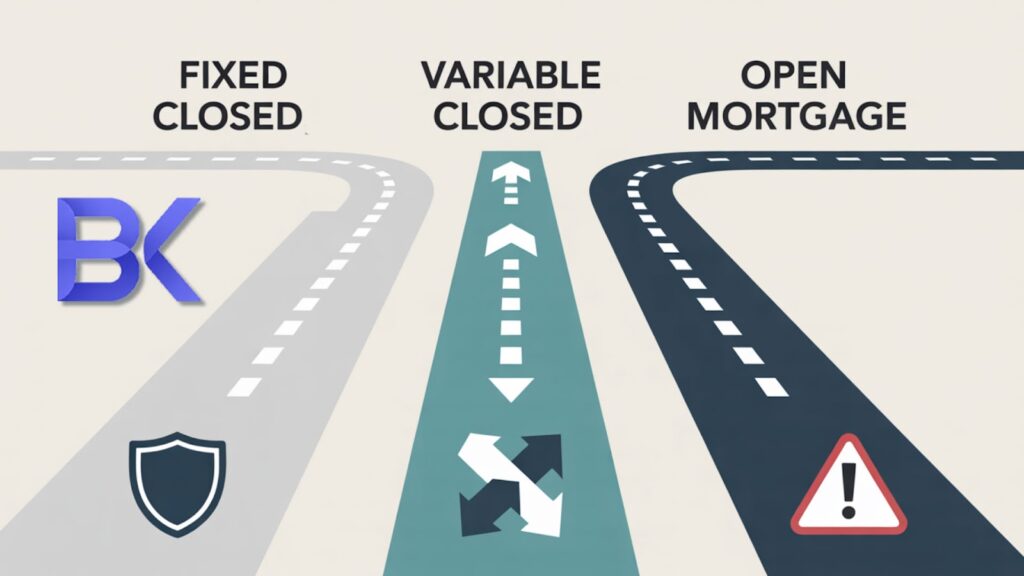
Open vs. Closed Mortgages: Understanding Your Flexibility
Quebec mortgages come with either open or closed conditions. Each option serves different borrower needs.
Key Features of Closed Mortgages
Closed mortgages offer lower interest rates but limit penalty-free prepayments. Most lenders permit annual lump sums (often 10–20% of the original principal) and modest increases to regular payments.
Exceeding these limits or breaking the mortgage early incurs a penalty. This structure suits homeowners planning to stay in the property for the full term.
Key Features of Open Mortgages
Open mortgages allow full or partial repayment anytime without penalty. They offer maximum freedom but come with higher rates. Open mortgages are often used when a borrower anticipates a large influx of funds, such as from a property sale, inheritance, or planned refinancing.
For most long-term owners, closed mortgages are more cost-effective. Open mortgages are best when an exit option is needed.
Mortgage Penalties: The True Cost of Breaking Your Contract
Prepayment penalties are a commonly misunderstood mortgage contract element. Yet, they can significantly influence the true cost of borrowing.
How Fixed-Rate Mortgage Penalties are Calculated
For most fixed mortgages, the lender charges the greater of:
• three months’ interest, or
• an interest rate differential (IRD).
IRD estimates the interest the lender loses if you break your mortgage early and they re-lend at today’s lower rate. When market rates drop significantly, IRD penalties can become substantial, sometimes thousands of dollars.
IRD penalties are often significantly higher with Big Banks compared to Monoline Lenders because of how they calculate their posted rates.
Understanding Variable-Rate Mortgage Penalties
Variable mortgages typically have a simpler penalty:
• three months’ interest on the remaining balance.
This difference is why variable mortgages remain appealing for borrowers expecting to refinance, move, or restructure before a typical term ends.
Understanding penalties is crucial. A mortgage with a slightly higher rate but low penalties can be cheaper than the lowest-rate option with strict exit costs.
Choosing Your Mortgage Structure in Quebec: Key Considerations
The optimal mortgage depends on your plans, not just the rate:
• If payment stability is a priority and you plan to live in the home for years, a fixed closed mortgage is generally the most predictable choice.
• If you anticipate change – a move, refinance, or major life shift – a variable mortgage or a shorter term can reduce long-term costs.
• If you know you will fully repay or restructure soon, an open mortgage may offer the necessary freedom.
• If unsure, choosing a shorter term or a flexible variable option keeps future choices open without restrictive, long-term commitments.
If you are buying your first home, make sure to also leverage the FHSA and HBP programs for your down payment.
A mortgage serves as both a financial product and a planning tool. The right choice aligns with your lifestyle, income stability, and comfort with payment fluctuations.
Mortgage Options in Quebec: A Quick Comparison
| Component | Fixed Closed Mortgage | Variable Closed Mortgage | Open Mortgage |
| Rate behaviour | Stays the same for the term | Moves with prime rate | Can be fixed or variable, usually higher |
| Payment stability | Fully stable | May change during term | May change, but can pay off anytime |
| Penalties | Greater of IRD or 3 months’ interest | Usually 3 months’ interest | None |
| Flexibility | Limited, subject to prepayment rules | Moderate; easier to exit than many fixed terms | High flexibility |
| Typical use | Long-term home, low risk tolerance | Buyers expecting movement or potential refinancing | Short-term ownership or incoming lump sum |
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between a mortgage term and amortization in Quebec?
A: Amortization is the total time it would take to pay off your mortgage in full (often 25–30 years), while the term is the shorter period (usually 1–5 years) during which your interest rate and contract conditions are locked in. At the end of the term, you renew or switch lenders, but your amortization schedule continues.
Q: When does a fixed-rate mortgage make more sense than a variable rate?
A: A fixed-rate mortgage is usually better if you prioritize payment stability, have a tight budget, or plan to stay in the property for most of the term. A variable rate can be attractive if you can handle payment changes and expect to move, refinance, or benefit from potential rate drops.
Q: How are mortgage penalties calculated if I break my contract early?
A: For most fixed-rate mortgages, the lender charges the greater of three months’ interest or an interest rate differential (IRD). For most variable-rate mortgages, the penalty is usually just three months’ interest on the remaining balance.
Q: When should I consider an open mortgage in Quebec?
A: Open mortgages are useful if you expect to repay or significantly reduce your mortgage in the short term – for example after selling a property, receiving an inheritance, or doing a major refinance. They allow full repayment at any time without penalties but usually come with higher interest rates.
Q: Can a mortgage with a slightly higher rate still be the cheaper option?
A: Yes. If that mortgage has lower prepayment penalties or more flexible terms, it can cost less over time than a lower-rate mortgage with strict conditions and expensive penalties for changes.
Ready to choose a mortgage structure that actually fits your plans instead of just chasing the lowest rate?
Book a free, no-obligation consultation with Boris Kolodner to compare fixed, variable, open, and closed options tailored to your situation in Quebec.
Call (514) 834-5558 or email contact@bkfinancialservices.ca to schedule your personalized mortgage review in English, French, Russian, or Hebrew.




